- Dr. Zankhana Shetty, Mumbai

- April 20, 2024
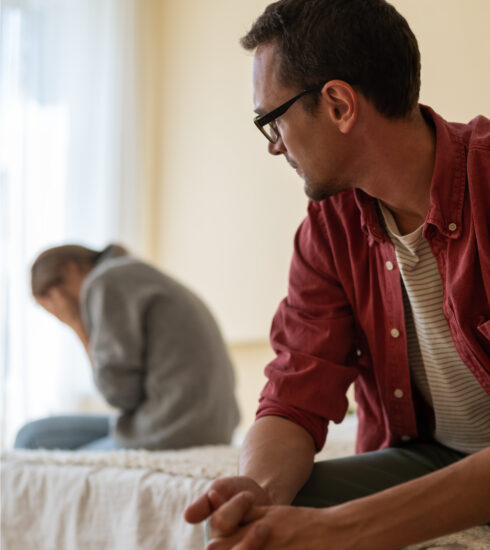
Women and Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder in which the body produces either too little insulin or cannot use available insulin efficiently, hence it cannot metabolize blood glucose effectively.
Incidence of diabetes in women?
About 382 million people have diabetes worldwide – approximately half of these are women. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), globally, 1 in 10 women has diabetes. Globally, diabetes is the ninth leading cause of death in women, causing 2.1 million deaths every year.
Do women have different symptoms of diabetes than men?
The common symptoms related to diabetes for both men and women are:
- Frequent urination
- Increased hunger
- Increased thirst
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Slow healing of wounds
- Weight loss
A few other symptoms that are specific to women only are:
- Vaginal infection
- Urinary tract infection
- Female sexual dysfunction.
However, it is important to keep in mind that many people with type 2 diabetes have no noticeable symptoms.
Reasons for diabetes and diabetes-related complications in women?
A few of the common reasons for the development of diabetes are:
- Hereditary
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity
Most women in our country have the tendency to ignore or neglect their health. Due to this, there is a delay in doctor consultation, a delay in screening for diabetes, and a delay in action by those in the pre-diabetes stage. Studies show that a delay in diagnosis is seen in at least 40% of cases. This puts them at risk of developing diabetes and diabetes-related complications.
Many women who belong to the lower socio-economic strata, have limited education, have poor access to healthcare, poor diet and consume tobacco are also at a high risk of developing the disease and related complications.
Diabetes-related complications in women?
Uncontrolled and long-standing diabetes may lead to complications like:
- Heart disease
- Blindness
- Kidney disease
- Urinary tract infections
- Vaginal infections
- Problems in getting pregnant.
- For women in menopause – further increase in blood glucose, weight gain, and sleep disorders.
What is gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is diabetes that develops during pregnancy and usually disappears after the birth of the baby. It can happen at any stage of pregnancy, but is more common in the second or third trimester. It usually happens when the body is not able to meet the extra need for insulin during pregnancy. It can cause problems for the mother and baby during pregnancy and after birth. Early detection is helpful.
Is it safe for a diabetic woman to get pregnant?
Yes, it is safe for women with diabetes to get pregnant. Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes can have a healthy pregnancy. They are advised to consult their doctor when they are planning their pregnancy. They should follow all precautions recommended by their doctor. They should request their doctor for a diabetes education program for a better understanding of diabetes.
What should women do to prevent or control diabetes?
To reduce the risk of diabetes, for better control of diabetes, and to prevent diabetes related complications, the “ABC“ approach has been recommended by the National Diabetes Education Program.
- A stand for the A1C, or HbA1c test, which measures average blood glucose over the previous two to three months.
- B is for blood pressure.
- C is for cholesterol.
Control your ABC by regular doctor consultation, lifestyle modification, healthy diet, exercise, and a healthy weight.