- Dr. Utsav Sahu, Delhi

- April 16, 2024
Know about Diabetes
How many types of diabetes?
Diabetes is mainly of two types:
Type 1 diabetes- which is usually seen in younger adults, where, due to autoimmunity, antibodies are formed that damage beta cells secreting insulin, leading to insulin deficiency. Also known as Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus.
Type 2 diabetes is a more common type of diabetes, where, due to insulin resistance, body organs like muscles and liver are not able to utilize sugar, which leads to high levels of sugar in the blood.
What are the earliest signs of diabetes?
- Frequent urination.
- Increased thirst.
- Feeling hungry.
- Feeling tired.
- Unintentional weight loss.
- Slow healing of wounds.
- Blurred vision.
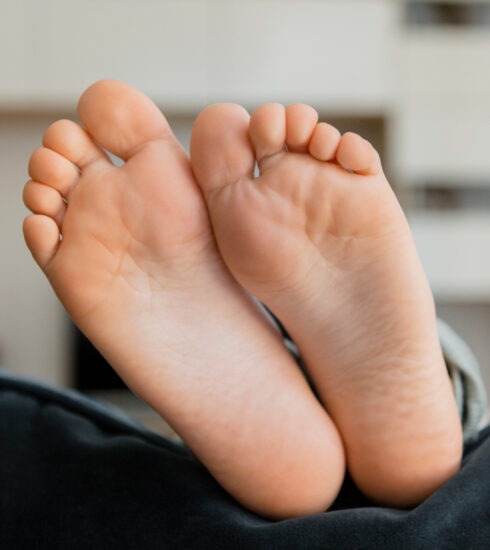
- Tingling & numbness of feet.
What happens to your body when you have uncontrolled diabetes?
If you do not treat your diabetes, the excess blood sugar can damage various organs of your body:
- Retina: Blurred vision and blindness
- Kidneys: Decreased urine, swelling over the body, ultimately leading to dialysis
- Nerves: Tingling & numbness, loss of sensation, wounds & ulcers
- Blood vessels: Increasing the risk of impotence, heart attacks & stroke by many folds.
Can eating too much sugar cause diabetes?
Sugar consumption will not directly cause diabetes but eating too much sugar can cause weight gain & obesity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
What is the main cause of type 2 diabetes?
Development of type 2 diabetes is related to lifestyle changes & genetics. Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity, weight gain, unhealthy eating practices & stress increase the risk. This risk increases further if there is any family history of diabetes in your parents or siblings.
Who are at increased risk of diabetes?
Your chances of having diabetes increase if you have a parent, brother, or sister with diabetes, if you are overweight or physically inactive, if you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol, if you had diabetes during pregnancy or if you are diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome.
How to manage your diabetes?
- Exercise regularly.
- Control your carbohydrate intake.
- Increase your fibre intake.
- Drink water & stay hydrated.
- Implement portion control.
- Choose foods with a low glycemic index.
- Control stress levels.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
- Take your medicines on time.
What is the glycemic index?
Glycemic index (GI) is a relative ranking of carbohydrates in foods according to how they affect blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates with a low GI value (50 or less) are more slowly digested, absorbed, & metabolized and cause a lower & slower rise in blood glucose.
- Low glycemic index food includes whole grains, oats, fox nuts, cashews, almonds, walnuts, skimmed milk, broccoli, mushrooms, tomatoes, lentils, chickpeas, green leafy vegetables, apples, oranges, cherries, strawberries & kiwi.
High glycemic index food includes sugar syrup, white bread, rice, boiled potatoes, French fries, cornflakes, ice cream, juices, watermelon, mango, grapes, pineapple, banana, & litchi.
How much exercise is advised for diabetes patients?
A diabetes patient is advised to do 30 minutes of daily exercise, which can include cycling or brisk walking. A brisk walk is defined as walking 100 metres in 1minute, which means covering 1 km in 10 minutes.
What is healthy weight loss & how much weight loss is required to control diabetes?
A 60 kg person needs 1800 to 2000 kcal per day. One needs to cut down 500 kcal per day to lose 1 pound or half a kg per week, which is referred to as a healthy weight loss. If one loses 3-5% of body weight, that means 2-4 kg in an 80 kg person, the diabetes control improves.